 |
|
LPCVD - low pressure CVD
- Because deposition takes place at lower pressure, and deposition rate depends on the gas partial pressure, one would think that the deposition rate is much lower
- However, because diffusion coefficient is inverse proportional with pressure, and the flow becomes molecular instead of viscous at low pressure, molecules will diffuse faster through the boundary layer, and the deposition will not be mass-transport limited, but reaction-limited.
- Wafers can be placed vertically and packed very closed, because the deposition is reaction-limited and does not depend much on flow transport
- Properties:
- lower cost ( due to higher throughput)
- superior films due to lower pressure, thus lower contamination and less gas-phase reactions
- Heating
- Hot walls (a more uniform temperature is inside the reactor, thus also uniform deposition)
- Cold walls (less deposition on walls, thus less gas consumed, but lack of uniformity at the edges of the wafers)
- NH3 is used for Si3N4 deposition instead of N2 due to the fact that it requires lower activation energy for dissociation
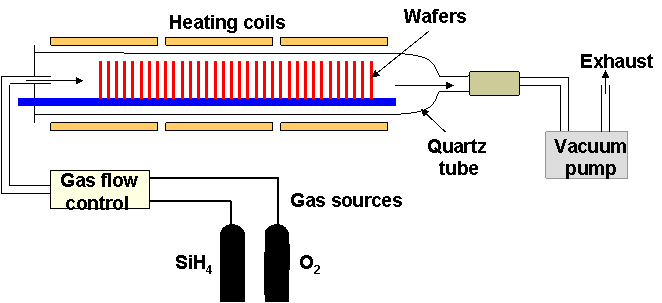
- Vertical reactor can be used for better uniformity (in the picture below an horizontal reactor is shown)
 |
|
