 |
|
MAGNETRON PLASMA
A magnetic field is introduced with the purpose:
- to increase the length of reactor (it actually increases the distance that an electron can travel before colliding with the walls) - when the magnetic field is parallel with the electric field
- Lorentz force, caused by the magnetic field curbs the electron trajectory, the resultant force will be:
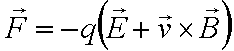
- The electron trajectory will look like in the picture below:
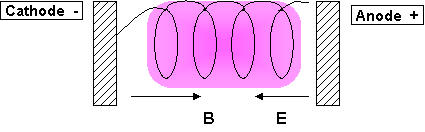
- The effect is that during this long path, the electron has time to absorb more energy from the RF source and the plasma efficiency increases
- It is used especially to ignite plasma at low pressure, when fewer collisions causes the electron to lose its energy at the walls before having the chance to ionise a molecule
- confide the electron movement close to the cathode - when the magnetic field is perpendicular on the electric field, as in the picture below:
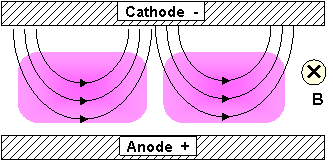
-
The plasma is very dense (high concentration of electrons, ions) around the cathode
-
Application: sputtering purposes, plasma at low pressure, etc.

|
|
