|
|
||
|
This are a few examples of deposition methods, using liquid sources:
During the deposition, there are no chemical reactions that take place, as in the case of chemical liquid deposition. The liquid source is solidified by different physical means. For example the solvent can be evaporated, resulting in a solid film.
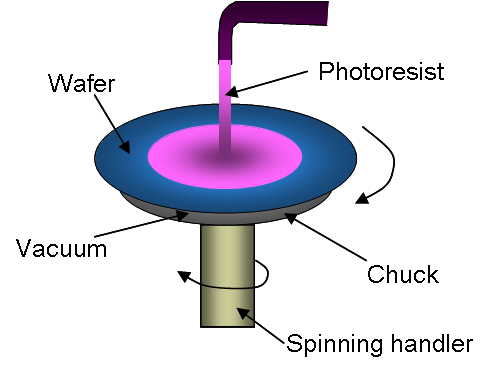
SPINNING (spin coating)
More information on spin casting can be found in the lithography tutorial, when application of photoresist is dicussed.
|
 Substrate preparation
Substrate preparation