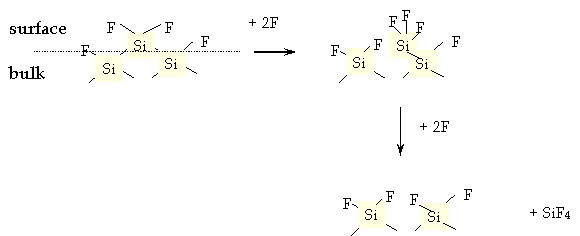
-
SiO2/Si selectivity
-
sometimes it is preferable to etch only the silicon, and not the underlying SiO2
-
in F2 ambient, the ratio between the etching rates for the two materials is Si:SiO2 = 50:1
-
Because F2 is not good for environment, it is prefered to use CF4 as etching gas, however CF3 etches more aggressively silicon oxide than F2, thus it is not very selective

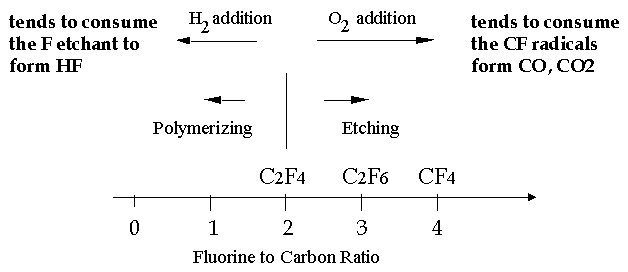
-
Si3N4 & Loading effect
-
To insure selectivity in relation to SiO2, CF4 - O2 ambient can be chosen (similar as in Si case)
-
To insure selectivity in relation to Si, CF4 - H2 ambient can be chosen
-
Loading effect
|
|
