 |
|
- STM (scanning tunneling microscopy)
- possible to deposit only on semiconductors and conductors
- system similar to AFM
- how is it done: a current is applied between tip and substrate
- the current density I ~ exp(-2ad), where d is the distance between tip and substrate
- by measuring the current it is possible to calculate d and to maintain the distance tip-substrate constant
- the substrate (Au, Si) is placed in a solution containing FeCo5
- due to the high electric field between tip and substrate, the molecules situated beneath the tip are dissociated and Fe is deposited on the substrate
- applications: nano-dots for single electron transistors
insert picture stm
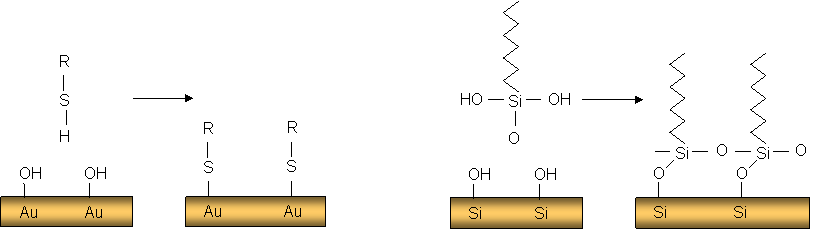
- SAM (self assembled monolayers)
- forms ordered chemisorbed films on surfaces from a solution
- synthesized from hydrocarbons chains (R) and functionalised with various reactive groups (sulfur, etc.)
- thiol (RSH) is a sulfur organic compund that is used often in SAM, due to its reactivity with Au surfaces
- H atom is removed and sulfur forms a covalent bond with the Au surface
- other compounds can be used to form bonds with Si surfaces, like in the right picture
- only one monolayer is deposited at a time
- applications: biomimetic membranes, MEMS
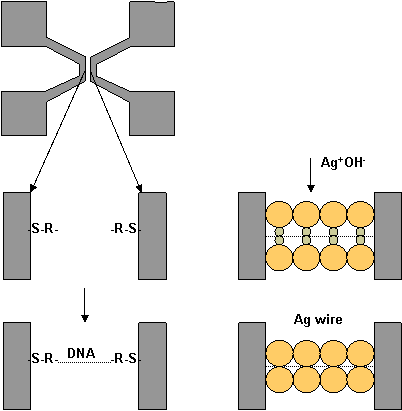
- DNA - based assembly
- DNA helics are connected by DNA strands, which consist of three components: phosphate, sugar and amine base (adanine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) or cytosine (C))
- the A base will hybridize only with a T base, and a G base will connect with the C base
- due to the DNA complementary nature, it can be used as a programmable recognition code in making structures
- application: DNA can be used as glue for nanowires fabrication (see picture), DNA strands are attached selectively to the substrate (to RSH compounds) when bias is applied, then the substrate is introduced in AgOH solution and a Ag wire is obtained
 |
|
