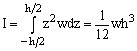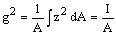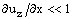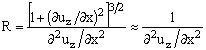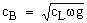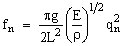Transverse Waves in a Bar
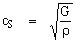 where
where 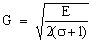 ... shear elastic modulus
... shear elastic modulus
- Torsional waves
- Velocity of torsional waves
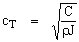 where J ... polar moment of inertia,
where J ... polar moment of inertia,
C ... constant depending on the cross-section geometry
- Bending waves
- More complex than the preceding mode
both longitudinal and transverse components are coupled
- Situation on a differential angular segment of a beam:
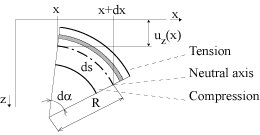
Internal stress in the x direction (linearly distributed):
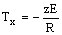
Total internal bending moment (M)
for a rectangular cross-section
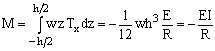 where I ... moment of inertia of the beam cross-section
where I ... moment of inertia of the beam cross-section
for a rectangular cross-section:
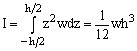
Radius of gyration of an area (g):
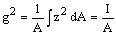
Radius of curvature (R)
- Is not in general constant
- Generally, for MEMS devices, displacements uz are limited to small values and
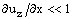
Approximate relation for the estimation of the radius R:
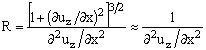
- Velocity of bending waves
supposing that the wavelength is large compared to transverse dimensions of the bar
satisfied in many MEMS applications
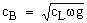
Boundary conditions for flexural waves in a bar:
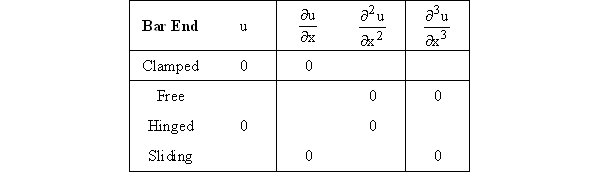
Frequencies of flexural modes
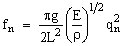
Quotients qn=2n/cB=2L/ln depend merely on the manner of fixing the bar
and on the order of the harmonic
Values of these quotients for the first few modes and for different beam supports are given in the following table
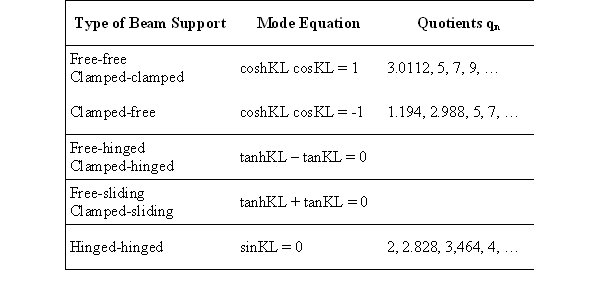

 Accelerometer
Accelerometer

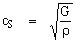 where
where 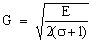 ... shear elastic modulus
... shear elastic modulus 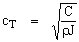 where J ... polar moment of inertia,
where J ... polar moment of inertia, 
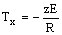
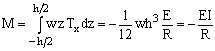 where I ... moment of inertia of the beam cross-section
where I ... moment of inertia of the beam cross-section