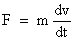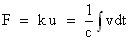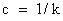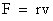Electro-mechanical Analogy
-
Hypothesis: mechanical system is composed of ideal components carrying either
-
Approximation that can be used under the condition that the system components are much smaller than the wavelength of an acting signal
-
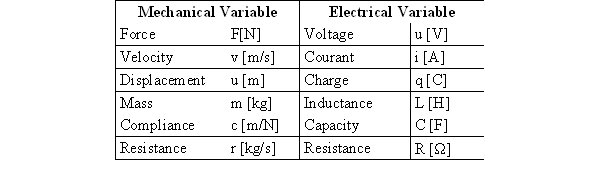
Basic variables used in the description of translational mechanical systems
-
Basic one-port components
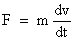
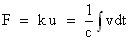
u ... displacement
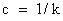
k ... spring factor
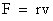
Mechanical system can be symbolized by a circuit composed of three basic elements as shown in the following figure:
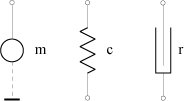
- Assignments of variables
- Force as an effort variable
- Velocity as a flow variable
- Conventions
- Effort-to-Voltage convention
Called electro-mechanical analogy I
or direct electro-mechanical analogy
Will be used in this course
- Flow-to-Voltage convention
Called electro-mechanical analogy II

 Accelerometer
Accelerometer