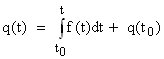|
|
||
|
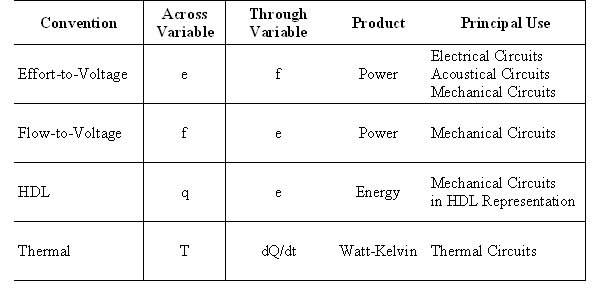
Different conventions are used for assignments of variables:
Examples: Electrical circuits uses the "effort-to-voltage" convention. Mechanical circuits uses both the "effort-to-voltage" and "flow-to-voltage" conventions. Acoustic circuits uses the "effort-to-voltage" convention. "HDL" circuit formulation uses an effort and a displacement as a pair of system variables.
Thermal energy domain models uses the temperature, T, as the across variable
Choice of convention used for a given physical domain and for a given type of device is not unique Any of the conventions can be used to reach the same conclusions about the device behaviour Important to check the assignment convention used by other authors when comparing their approaches
|
 Accelerometer
Accelerometer