|
|
||
|
In the case of discrete components the minimum logical unit coincides with the constructive unit –package. A package = may contain several logical parts (entities or gates) having in this case a footprint with mire entities- multi part package. Each package will have on the PCB a unique name (Part Reference) which represents a unique prefix in the electronic schemetic.
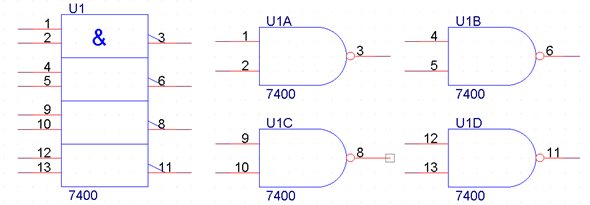
For example, if the integrated circuit SN7400 is used in a schematic and we suppose the IC7 prefix, then the four component parts will be refered as IC7A, IC7B, IC7C, IC7D if we count alfanumeric or IC7-1, IC7-2, IC7-3, IC7-4 if the indexing is done numeric. If the parts contained in a footprint have the same graphical representation then one can say we have a homogenous package. Contrarly, the package is heterogenous. Normally the majority of packages from the ORCAD libraries are homogenous (all the entities from the footprint are identical) There are cases when the entities from the footprint are not identical and the part is heterogenous.
Fig. 6 ORCAD parts example
|
 Schematic design of PCB projects
Schematic design of PCB projects