 |
|
DIFFRACTION
-
Notions of diffraction are needed, because when light passes through small openings of the mask, it can be diffracted (light goes behind the corners), and the light intensity on the resist will change
-
The light can be characterised by: 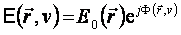
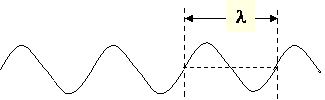
-
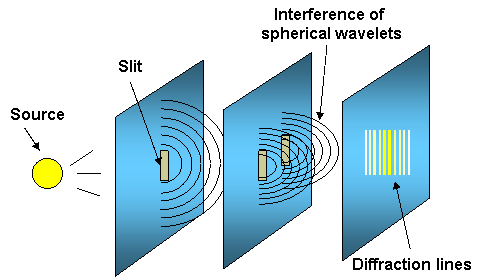
Huygen's principle says that a local disturbance generates spherical wavelets that will interfere
-
Diffraction occurs when light hits edges of objects. Thus it has a higher impact when the openings of the masks are small (for making small devices), and a lot of edges will be in the light's way
-
Diffraction bands are observed when light waves pass through narrow slits.
-
When the light passes through the small windows of the mask, it will be diffracted, and the light intensity that will fall on the photoresist will differ in the created diffracted bands (maximum intensity in the middle, then the intensity has peaks - first order, second order, etc. of interference - see picture below)
-
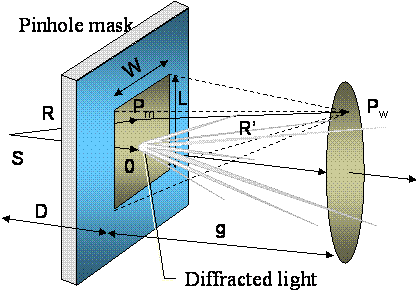
We will calculate the light intensity after light passes through an window, and how the window dimension influences it: (S - source, D - distance source -mask, g - distance mask - wafer, W, L - dimensions of the opening)
|
|
