|
|
||
|
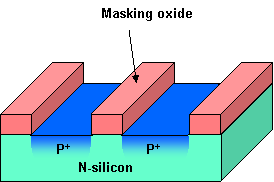
DEFINITION: Motion of particles due to difference in concentration. Application: Introducing dopant atoms (impurities) in a layer, in order to change the electrical conductivity. A structure with regions of different conductivities can be fabricated. Examples: pn junction, bipolar transistor, MOS transistor, etc. In the lower picture, a MOS transistor was fabricated, by doping with boron atoms two regions in the silicon. Originally the silicon was n-type (doped with phosphorous atoms), after diffusion the two regions became p-type silicon (source and drain of the transistor) .
|
 Substrate preparation
Substrate preparation