PARAMETERS THAT INFLUENCE DIFFUSIVITY
-
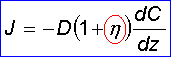
Diffusion constant or diffusivity is a paramater that appears in Fick's first law 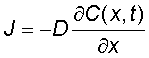 , giving the dependence of flux on concentration gradient.
-
Depends on:
-
Diffusion mechanism - the interstitial mechanism is faster than substitutional (atomistic models of diffusion), due to the fact that the impurities can travel further through the interstitials without requiring much energy.
-
Temperature - with increasing the temperature, the diffusivity increases, because the atoms thermal energy increases, thus they can diffuse faster
-
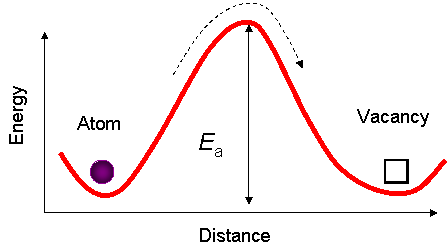
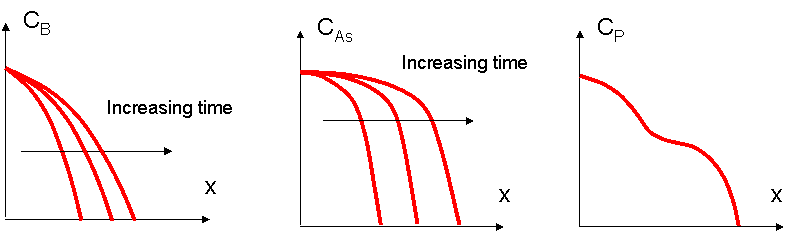
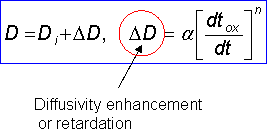
Diffusivity depends on temperature following an Arhenius type formula: 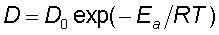 , where E a is the activation energy = the energy required to break the bonds between the atoms. (see picture below)
 |
|
