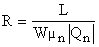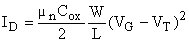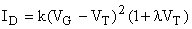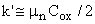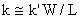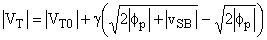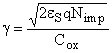|
|
||
|
MOSFET Analysis
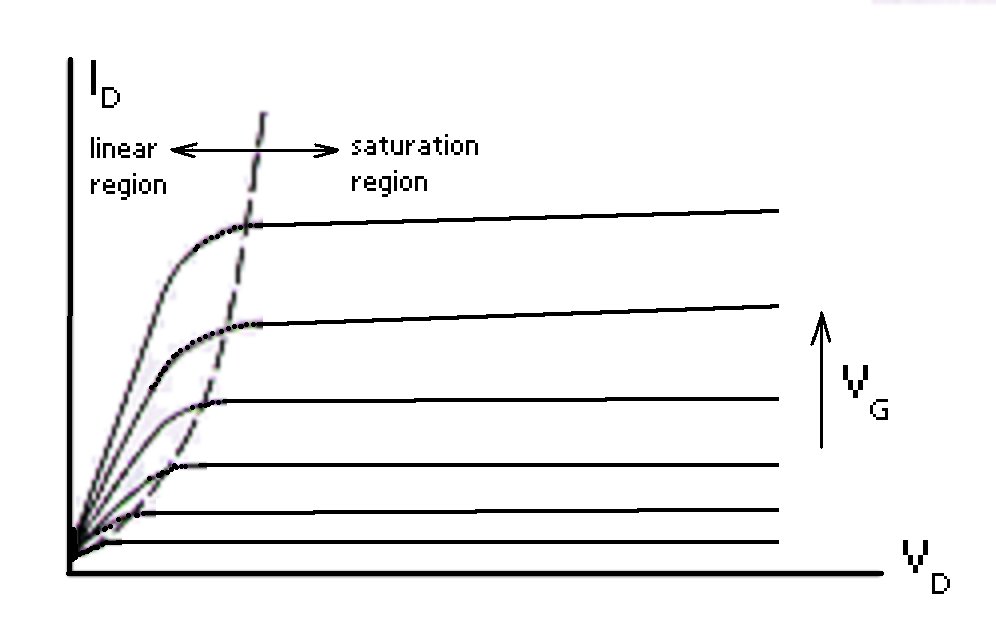
Voltage characteristics of an MOS transistor
Principal regions of voltage characteristic Linear region (triode region) (VD < VG - VT) Transistor acts as a resistor
L ... Length of the channel W ... Width of the channel μn ... Mobility of the electrons in the channel Qn ... Charge density of the electrons in the channel Resistance R is controlled by VG as Qn is depending on VG Saturation region (active region) (VD ≥ VG - VT) Drain saturation voltage VDsat = VG - VT Drain current ID ~ independent of VD
Cox ... Capacitance per unit area of the oxide layer Channel-length modulation Increase of the drain current with channel length reduction Approximation of the preceding formula:
l ... device constant depending on L, doping concentration, ... for L ~ 10 μm, l ~ 0.03 V -1 usual abbreviations:
Body effect
Key limitation of MOSFETs used as analogue circuit elements Assumption vSB = vS - vB = 0 is not valid (vB ... bulk (substrate) voltage) Threshold voltage of an n-channel transistor:
VT0 ... threshold voltage for vSB = 0 g ... device constant (often called as body-effect constant)
eS = e0 KS ... permittivity of silicon (KS ≈ 11.7) q ... electron charge (q = 1.6 10-19C) Nimp ... density of the impurity ions in the bulk (Nimp = Na for NMOS, Nimp = Nd for PMOS) Cox ... oxide capacitance Fp ... material constant of the bulk ~ 0.3 V
|
 Analogue filter
Analogue filter