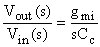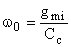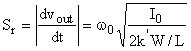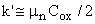|
|
||
|
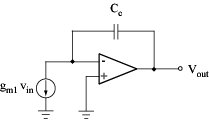
Case: internally compensated opamp with a pole-splitting capacitor Small input signals: - transistors operate in their saturation regions - small-signal models can be used - for moderate frequencies (|sp1| << w << |sp2|) o input stage Q1 - Q5 can be replaced by a frequency-independent voltage controlled current source o stages Q6 - Q11 can be replaced by a frequency-independent amplifier with the feedback capacitor Cc connected between its input and output terminals o corresponding model:
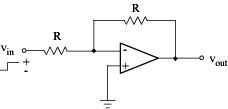
High-frequency gain: Unity-gain frequency: Case: voltage inverter
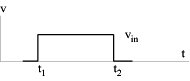
Supposing a step voltage on the input:
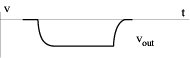
Output voltage For small input amplitude (much less than 1 V): Exponentially varying waveform
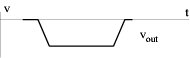
For large input amplitude ( ~ 5 V): Nearly linear rise and fall slewing
Slew rate ... slope
w0 ... Unity gain frequency I0 ... Bias current of the input stage
L ... Length of the channel W ... Width of the channel
Related Gregorian, R., Temes G. C., Analog MOS integrated circuits for signal processing, Wiley, 1986. Johns, D. A., Martin, K., Analog integrated circuit design, Wiley, 1997. Razavi, B., RF Microelectronics, Prentice Hall, 1998. Carter, B., Brown, T.R., Handbook of operational amplifier applications, Application Report, Texas Instreuments, 2001.
|
 Analogue filter
Analogue filter