 |
|
||
|
Stability:
|kAv (jw180)| < 1 No sp can occur on the jw-axis Gain margin - measure of stability
Gain margin (in dB) = 20 log |kAv (jw180)|
w0 ... frequency at which the monotone decreasing absolute value of a loop gain |kAv (jw)| reaches the value 1 (0 dB) ... unit gain frequency Another sufficient condition of stability:
Phase margin - measure of stability
Stability conditions can be checked by using the Bode plots: At the unity-gain frequency w0:
m is the number of those poles whose magnitude |si| is less than w0 For a substantial positive phase margin
60o ~ : 90o m = 1
|
 Analogue filter
Analogue filter

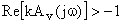
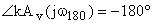
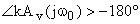
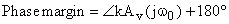
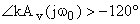 m should be less than 2
m should be less than 2