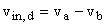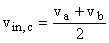|
|
||
|
Main differences between the ideal opamp and a real device:
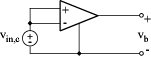
Differential gain: AD = A Common-mode gain: AC = vo / vin,c
measured as shown in following figure:
CMMR = AD / AC Or in logarithmic units:
20 log10 (AD / AC) in dB Common-mode signals undesirables CMRR measures the degree of suppression of these signals Requirement: large value of CMRR Typical values for MOS amplifiers CMRR ~60-80 dB
Gain A decreases at high frequencies Evaluation by the frequency f0 at which |A(f0)| = 1 Typical values for MOS amplifiers f0 ~1-10 MHz
For a large input step voltage, the output follow the input at a slower finite rate (reason: some transistors may be driven out of their saturation regions) Slew rate: maximum rate of change dvo/dt No direct relation with the frequency response Typical values for MOS amplifiers ~1-20 V/?s
Open-loop output resistance is nonzero, resistive Typical values for MOS amplifiers with an output buffer ~0.1-5 kW Affects the speed of charging a capacitor connected to the output
Noise generated by the MOS transistors measured on the output of an opamp, von, can be modelled by an equivalent Typical values of the equivalent input noise source in a wide band (10 Hz to 1 MHz) for MOS amplifiers ~10-50 ?V RMS Achievable values of the equivalent input noise for bipolar amplifiers ~3-5 ?V RMS
Defined as 20 log 10(vin, max / vin, min) in dB vin, max ... maximal input signal amplitude in which the device can handle Optimistic estimate: vin, max ~ VCC /A (+-VCC ... power supply voltages, A ... open-loop gain) vin, min ... maximal input signal Dynamic range of an opamp in open-loop conditions ~ 30 - 40 dB Dynamic range of an opamp in negative feedback configuration can be much larger
Incremental component v of the power source gives the corresponding voltage Apv on the on the opamp output PSRR = AD / Ap (AD = A ? differential gain) Or in logarithmic units: Typical values for a single MOS amplifier PSRR ~60-80 dB
Typical values for an MOS opamp range from 0.25 to 10 mW dc power drain
|
 Analogue filter
Analogue filter