 |
|
||
|
Design of a filter with specified characteristics based on following definition Different ways of approximating the ideal "brick wall" filter:
o Defined by
W ... normalized frequency Wc ... cutoff frequency o Maximally flat filter magnitude responses with no consideration of phase linearity or group delay considerations o DC gain is 1 o Magnitude response is a monotonically decreasing function of frequency o No ripples
o The most linear phase response of all IIR filters with no consideration of the frequency magnitude response o Maximally constant group delay
o Passband, or stopband, ripples constrained within fixed bounds o Two families
o Cannot have ripples in both the passband and the stopband o Have steeper transition region roll-off
o Sharpest roll-off for a given number of filter coefficients o Poorest phase linearity of the most common IIR filter design functions o Ripple in passband and stopband are equal Two categories of analogue filters
|
 Analogue filter
Analogue filter
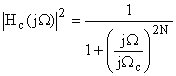 N ... filter order
N ... filter order