|
|
||
|
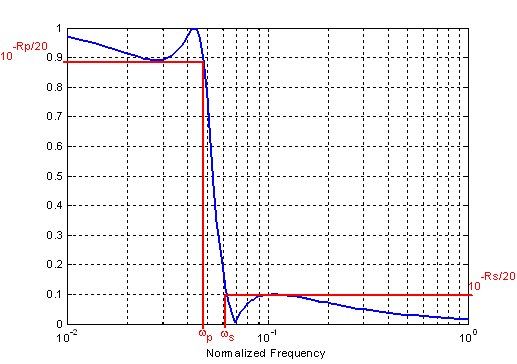
Filter specifications
o Upper passband frequency for low-pass filters o Lower passband frequency for high-pass filters o Determined by the -3dB point of a filter magnitude response relative to a peak passband value
o Frequency width of the passband of a filter o For a low-pass filter the bandwidth is equal to the cutoff frequency o For a band-pass filter
o For low-pass and high-pass filters with Q>3 can be graphically presented as o For a band-pass filter is defined as the reciprocal value of the relative bandwidth
o Difference in phase at a particular frequency, between an input sine wave o For an ideal filter the phase response is linear with the frequency
o Derivative of a filter phase with respect to frequency o Can be thought as the propagation time delay of the envelope of an amplitude modulated signal o For an ideal filter the group delay is constant
o Fluctuations or variations in the frequency magnitude response within the passband of a filter o Measured in dB
|
 Analogue filter
Analogue filter