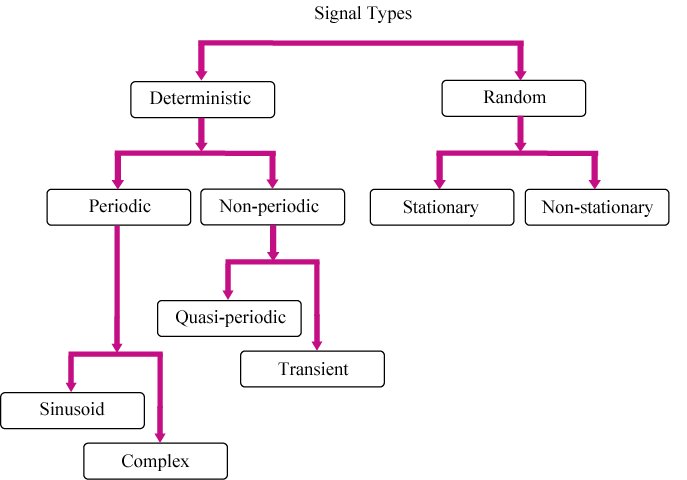
Signal types:
Periodic
In the simplest form are sinusoidal, that is, consisting of a single sine wave (pure tone).
Complex periodic signals (also known as complex tones) are composed of multiple sinusoidal components.
All these frequencies are multiples of some fundamental frequency
Pseudo-random signal
-
Particular type of periodic signal
-
Sometimes used to simulate random signals
-
Periodic time is very long
-
Can be reproduced exactly - benefit in testing
Non-periodic
Quasi-periodic
Frequencies of the various sinusoids are not harmonically related.
Transient
Occur only once or very infrequently. Their starts and terminate at a value equal to 0.
Examples
Slamming a door
Shock wave generated from an impact test
Stationary
Average properties do not vary with time - independent of the particular sample record
Examples
Thermal noise at constant temperature
Non-stationary
Statistical properties change significantly over the observation window
Examples
Jet engine noise
Machine tool vibrations
Earthquake motions
Speech